How to Turn On or Off HDR and WCG Color for a Display in Windows 10
The Windows 10 operating system includes support for HDR videos (HDR). The HDR video format eliminates various limitations of classic SDR video signals and adds a greater brightness and color to the picture.
HDR-capable devices, e.g. displays and TVs, can read that meta data to show a bright colorful image. The metadata can be used to show very bright and very dark areas simultaneously, so the image retains its natural contrast without appearing too dark or too whitened.
Due to the display having the capability to show a lot of shades between white and black, an HDR display can also show a greater variety of shades for other colors. This becomes a really great feature when you are watching videos related to nature or some color-rich scenes. If your device comes with an HDR display, Windows 10 is able to utilize it to show better colors.
Wide Color Gamut (WCG) is an enhancement that allows showing a more vivid picture by expanding the color space. It extends the color palette and makes colors more realistic and vibrant by increasing the range of values in the color spectrum. With it, your display can show up to one billion colors!
To Turn On HDR and WCG Color for Display in Windows 10,
- Open the Settings app (Press Win + I on the keyboard).
- Go to System -> Display.
- On the right, click on the Windows HD Color settings link.
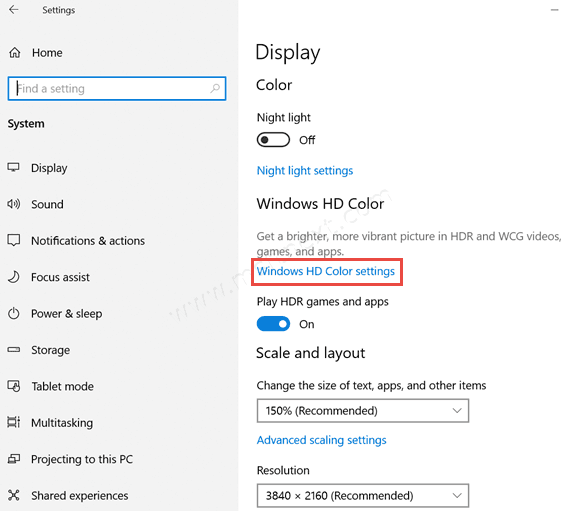
- On the next page, select the required display in the Select a display to view or change the settings for it list if you have more that one display connected.
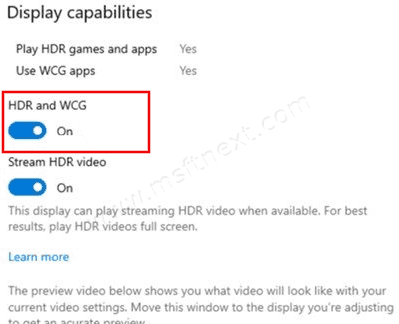
- Under the Display capabilities section, you will be able to enable or disable the HDR and WCG options using the appropriate toggle switch.
- You are done!
I suggest you to learn more about display requirements for HDR videos in Windows 10. They are listed below.
HDR video Display requirements in Windows 10
To play streaming high dynamic range (HDR) video in Windows 10, the built-in display for your laptop, tablet, or 2-in-1 PC needs to support HDR. To find the specifications for a specific laptop or tablet, visit the device manufacturer’s website. Here are the requirements:
- The built-in display needs to have a resolution of 1080p or more, and a recommended max brightness of 300 nits or more.
- The Windows 10 device needs to have an integrated graphics card that supports PlayReady hardware digital rights management (for protected HDR content), and it must have the required codecs installed for 10-bit video decoding. (For example, devices that have a 7th Generation Intel Core processor, code-named Kaby Lake, support this.)
External displays
- The HDR display or TV must support HDR10, and DisplayPort 1.4 or HDMI 2.0 or higher.
- The Windows 10 PC needs to have a graphics card that supports PlayReady 3.0 hardware digital rights management (for protected HDR content). This could be any of the following graphics cards: NVIDIA GeForce 1000 series or higher, AMD Radeon RX 400 series or higher, or Intel UHD Graphics 600 series or higher. A graphics card that supports hardware-accelerated 10-bit video decoding for HDR video codecs is recommended.
- The Windows 10 PC must have the required codecs installed for 10-bit video decoding (for example, HEVC or VP9 codecs).
- It is recommended that you have the latest WDDM 2.4 drivers installed on your Windows 10 PC. To get the latest drivers, go to Windows Update in Settings, or check your PC manufacturer’s website.
Also, see
How To Calibrate Display For HDR Video In Windows 10
That’s it.
