In this tutorial, you will find instructions on how to add Windows Security to the Windows 10 context menu. Using it, you can literally in one click open the desired section of this application.
The standard antivirus, Windows Defender, which is more than enough for the average user to keep the system safe, is integrated into a new application in Windows 10. It’s called Windows Security, and it’s located in the Start menu and in the notification area next to the clock.
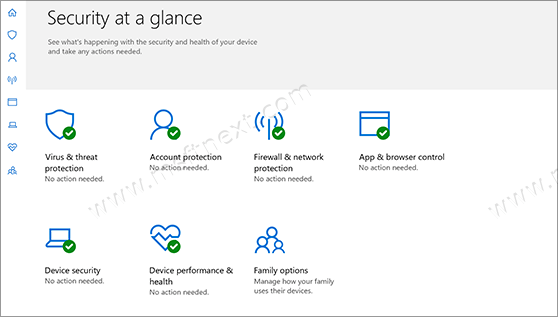
For more convenient and faster access you can add it to the context menu, so that you can get quick access to antivirus, firewall, performance monitoring, and a number of other useful utilities, just by right-clicking on the desktop.
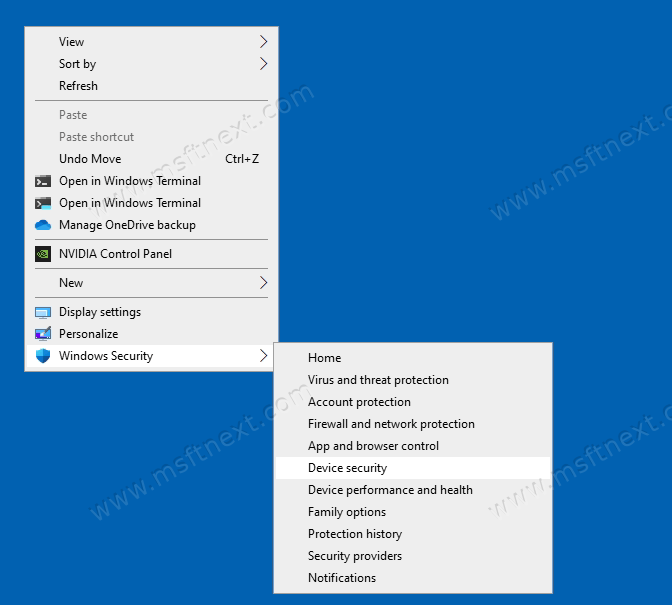
You can add any item you need to the Windows context menu by editing the operating system registry. In the case of Windows Security, a lot of changes need to be made. To simplify the procedure, we provide ready-made registry files that will do everything for you.
In this guide, you will find instructions on how to add Windows Security to the desktop context menu.
- Download the ZIP archive with two registry files from this link.
- Unpack the archive into any folder convenient for you. You can extract them directly to your desktop folder.
- Double-click the Add_Windows_Security_desktop_context_menu.reg context menu and confirm the system registry change.
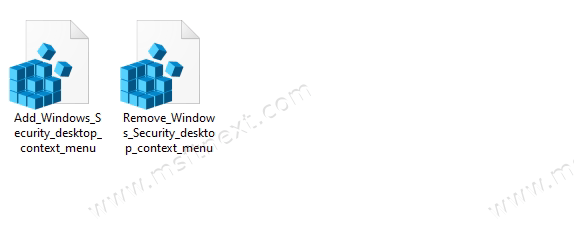
After that, an additional item, Windows Security, will appear in the context menu of the desktop. If you want to restore everything to its original state, run the Remove_Windows_Security_desktop_context_menu.reg context menu and confirm the addition to the registry.
How it works
Every modern application in Windows 10 has its own unique identifier address, also known as a URI. You can run the application by entering its URI in the Run window, which is invoked by the Win + R buttons or from the command line. The registry file contains some sort of link to the command to execute one of several Windows Defender URIs. Here is a detailed list of them.
-
windowsdefender:– home page of the application. -
windowsdefender://threat– protection against viruses and threats. -
windowsdefender://account– account protection. -
windowsdefender://network– firewall and network security. -
windowsdefender://appbrowser– control applications / browser. -
windowsdefender://devicesecurity– device security. -
windowsdefender://perfhealth– device performance and health. -
windowsdefender://family– parameters for the family. -
windowsdefender://history– protection history. -
windowsdefender://providers– system and security updates. -
windowsdefender://settings– notification settings.
Done.
