How to view BIOS boot time in Windows 10. Windows 10 has a built-in timer that measures the boot time of the computer’s BIOS. With this metric, you can measure the performance of your computer and monitor how certain devices affect power-on time.
BIOS (also known as firmware) is a special low-level motherboard software that, simply speaking, is responsible for initializing and managing your computer’s components (this process is also called POST). When you press the computer’s power button, a Power-on self test occurs. During this test, the BIOS initializes all parts of the computer and then transfers control to the operating system.
BIOS is an outdated technology and concept. The BIOS in modern computers has been replaced by a newer firmware version – UEFI. UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) got rid of BIOS restrictions, such as disk limits or memory consumption. Nevertheless, many users out of habit hereinafter referred to as UEFI BIOS. In fact, even the Windows 10 operating system itself in the Task Manager refers to UEFI as BIOS.
Please note: the timer reviewed in this article determines the time from the start of the computer to the transfer of control of the hardware components to the operating system. In other words, this period does not include the start of the operating system itself. In addition, the collected value can suddenly rise from a few seconds to several minutes. This happens if, before turning on the computer, you spent some time in the BIOS / UEFI to change settings, overclock, or for any other purpose.
View BIOS boot time in Windows 10
- Open the Task Manager.
- If you have the compact mode of the Task Manager enabled, click on the More details button in the lower left corner.
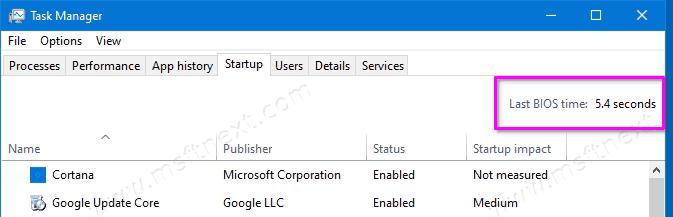
- Go to the Startup tab.
- Look in the upper right corner for the duration of the last BIOS run. The time in seconds will be displayed to the right of the Last BIOS time label.
Keep in mind that not all computers display the last BIOS boot time. Microsoft does not have official documentation on this feature, but practice shows that it is available on more modern devices with motherboards that support UEFI. In addition, Windows will not measure startup time if the UEFI-compatible board is in BIOS Compatibility Mode. Also keep in mind that this feature is not present on Windows 7 – it is part of the new Task Manager that debuted with Windows 8.
How to reduce the boot time of BIOS
Computer startup time is a topic for a separate article or even a whole series of materials. There are many ways to speed up computer startup and BIOS startup (these are separate concepts).
Often, the duration of the last BIOS start is affected by the number of components in your computer and the settings of the BIOS / UEFI itself. On ultrabooks without a lot of peripherals, the time from start to transfer of control to the system can take less than two seconds, since the motherboard does not need to initialize a large number of components.
On gaming computers or workstations, this period will be longer, since the BIOS must test all additional devices – video card, capture card, sound card, and so on. The more devices, the longer the BIOS startup time.
Finally, this parameter is affected by settings of the BIOS itself – the operating system boot order, Legacy mode, full-screen motherboard logo, and so on. You can reduce boot time by a few seconds by optimizing your BIOS settings. For example, exclude all third-party device initialization from the boot menu, disable unnecessary peripherals and ports, and the motherboard logo. The end result depends on individual features and devices of your computer.
